Welcome to the COMPETITIVE EXAM MCQs SERIES of ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE for UGC-NET/JRF, SLET, GATE, and other entrance tests – Agro-climatic zones of India.
Agro-climatic Zones of India deal with India’s geographical regions based on climatic conditions, soil types, and topography, which significantly influence agricultural practices and crop selection. Therefore, It is an important subject for Indian competitive examinations.
Syllabus outline
- Definition and significance of agro-climatic zones in agricultural planning.
- Historical development and classification methods.
- Climatic parameters affecting agricultural productivity (temperature, precipitation, humidity, and wind patterns).
- Soil types, fertility, and water availability in different regions.
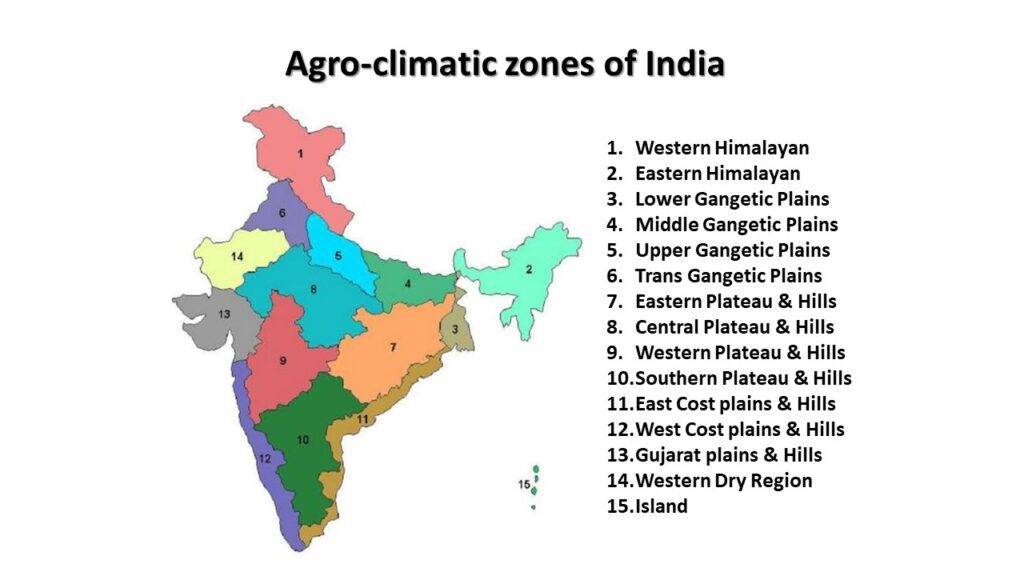
- Overview of the various agro-climatic zones in India and their characteristics.
- The division of India into different zones based on climate, soil, and topography.
This quiz contains the concept-based most frequently asked 25 MCQs of “Agro-climatic zones of India“. Each question has a single correct/most appropriate answer.
1. Which agro-climatic zone in India is known for coarse cereals like pearl millet and sorghum?
a) Western Dry Region
b) Eastern Plateau and Hills
c) Gangetic Plain Region
d) Gujarat Plains Region
2. The Western Rajasthan Desert agro-climatic zone is famous for which crop?
a) Oilseeds
b) Pulses
c) Wheat
d) Cotton
3. Which agro-climatic zone in India is highly suitable for temperate fruit cultivation like apples and pears?
a) Western Himalayan Region
b) Southern Plateau and Hills
c) Western Dry Region
d) Eastern Himalayan Region
4. Which agro-climatic zone is characterized by its cold climate and is known for apple and potato cultivation?
a) Eastern Himalayan Region
b) Western Himalayan Region
c) Western Dry Region
d) Southern Plateau and Hills
5. Assertion (A): The Punjab Plains agro-climatic zone is known for its extensive wheat cultivation.
Reasoning (R): The Punjab Plains receive sufficient irrigation from the Indus and its tributaries, making it favourable for wheat cultivation.
a) Both A and R are true, but the R is not the correct explanation of the A.
b) Both A and R are true, and the R is the correct explanation of the A.
c) The A is true, but the R is false.
d) The A is false, but the R is true.
6. Assertion (A): The Western Coastal Region of India is suitable for coffee and black pepper cultivation.
Reasoning (R): The Western Coastal Region receives heavy rainfall and has a tropical climate, creating favourable conditions for coffee and black pepper cultivation.
a) Both A and R are true, but the R is not the correct explanation of the A.
b) The A is true, but the R is false.
c) Both A and R are true, and the R is the correct explanation of the A.
d) The A is false, but the R is true.
7. The Bundelkhand agro-climatic zone is suitable for which crop cultivation?
a) Rice
b) Pulses
c) Wheat
d) Oilseeds
8. The Bihar Plains agro-climatic zone is famous for which crop cultivation?
a) Cotton
b) Rice
c) Pulses
d) Wheat
9. Which agro-climatic zone is characterized by its hot and humid climate, making it suitable for sugarcane and jute cultivation?
a) Gujarat Plains Region
b) Southern Plateau and Hills
c) Western Coastal Region
d) Eastern Coastal Region
10. India’s Western Dry Region agro-climatic zone is known for which crop cultivation?
a) Millets
b) Pulses
c) Jute
d) Sugarcane
11. Which agro-climatic zone in India is highly suitable for spices like cardamom, ginger, and turmeric cultivation?
a) Western Himalayan Region
b) Western Coastal Region
c) Eastern Plateau and Hills
d) Eastern Coastal Region
12. Which agro-climatic zone in India is more suitable for tropical fruits like papaya and pineapple cultivation?
a) Eastern Coastal Region
b) Eastern Plateau and Hills
c) Western Coastal Region
d) Gangetic Plain Region
13. The North-Eastern Hills Region agro-climatic zone is famous for which crop cultivation?
a) Rice
b) Tea
c) Cotton
d) Jute
14. The Odisha Plains agro-climatic zone is known for which crop cultivation?
a) Rice
b) Wheat
c) Pulses
d) Cotton
15. Assertion (A): The Gangetic Plain Region in India is characterized by its fertile alluvial soil, making it suitable for rice cultivation.
Reasoning (R): The Gangetic Plain Region receives abundant rainfall and is drained by several rivers, including the Ganges, providing ideal conditions for rice cultivation.
a) The A is true, but the R is false.
b) The A is false, but the R is true.
c) Both A and R are true, but the R is not the correct explanation of the A.
d) Both A and R are true, and the R is the correct explanation of the A.
16. The Central Plateau and Hills agro-climatic zone is known for its cultivation of which crop?
a) Sugarcane
b) Millets
c) Oilseeds
d) Pulses
17. Which agro-climatic zone in India is more suitable for tropical fruits like mango and banana cultivation?
a) Eastern Plateau and Hills
b) Gangetic Plain Region
c) Western Coastal Region
d) Eastern Coastal Region
18. Assertion (A): The Odisha Plains agro-climatic zone is suitable for rice and oilseed cultivation.
Reasoning (R): The Odisha Plains receive substantial rainfall from the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea branch of the monsoon, creating favourable conditions for rice and oilseed cultivation.
a) The A is true, but the R is false.
b) Both A and R are true, but the R is not the correct explanation of the A.
c) Both A and R are true, and the R is the correct explanation of the A.
d) The A is false, but the R is true.
19. Which agro-climatic zone is characterized by its hilly terrain and is known for temperate fruits like orange and apple cultivation?
a) Eastern Himalayan Region
b) Western Dry Region
c) Southern Plateau and Hills
d) Western Himalayan Region
20. Assertion (A): The Rayalaseema agro-climatic zone is suitable for oilseed and pulse cultivation.
Reasoning (R): The Rayalaseema region in Andhra Pradesh, India, has a semi-arid climate with moderate rainfall, which is conducive to oilseed and pulse cultivation.
a) The A is true, but the R is false.
b) Both A and R are true, and the R is the correct explanation of the A.
c) Both A and R are true, but the R is not the correct explanation of the A.
d) The A is false, but the R is true.
21. Which agro-climatic zones in India are known for tropical fruits like mango, banana, and coconut production?
a) Eastern Plateau and Hills
b) Western Dry Region
c) Southern Plateau and Hills
d) Western Himalayan Region
22. Which agro-climatic zone is known for aromatic rice varieties like Basmati cultivation?
a) Western Himalayan Region
b) Gangetic Plain Region
c) Eastern Himalayan Region
d) Eastern Coastal Region
23. The North-Western Rajasthan Desert agro-climatic zone is suitable for which crop cultivation?
a) Pulses
b) Wheat
c) Oilseeds
d) Cotton
24. The Gujarat Plains agro-climatic zone is suitable for which crop cultivation?
a) Tea
b) Cotton
c) Jute
d) Millets
25. Which agro-climatic zone is characterized by its cold and dry climate, making it suitable for the cultivation of barley and rapeseed?
a) Eastern Himalayan Region
b) Southern Plateau and Hills
c) Western Dry Region
d) Western Himalayan Region
Previous: Bio-geographic provinces of the world
Next: Principles of remote sensing and GIS
References
- P. K. Mishra (2019) Agro-Climatic Regions of India, Agrotech Publishing Academy, 1st edition.
- M. S. Swaminathan (2008) Sustainable Agriculture: Towards Food Security, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, 1st edition.
- V. D. Sharma (2014) Agro-Ecological Regions of India, National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning, 1st edition.
- Anil K. Tyagi (2018) Environmental Science and Engineering, Khanna Publishers, 3rd edition.