At present, we are facing many environmental challenges, from climate change to pollution. These issues raise important questions that we’re still working to answer. In this article, we’ll explore 15 unanswered environmental questions, why they matter, how they impact our planet and their scientific hypotheses. This article can provide directions for ongoing work needed to protect our environment for the future.
- What is the true extent of biodiversity on Earth?
- Why scientific forecasts of weather events are inaccurate?
- Why can’t we measure and appraise the cost of ecosystem services?
- Why indigenous and traditional practices of environmental conservation are not protected?
- Why current environmental awareness programs are ineffective?
- What are the true reasons for climate change?
- What is the ultimate fate of plastic pollution?
- Why is it challenging to control environmental infodemics?
- What role do humans play on planet Earth?
- How do pollutants affect consciousness?
- Why Earth’s magnetic poles are shifting rapidly?
- Does life exist beyond planet Earth?
- What is the actual process responsible for the origin of life on Earth?
- What were the actual reasons behind the decline of the impressive Polynesian civilization on Easter Island?
- Do exoplanets affect human health and the environment?
1. What is the true extent of biodiversity on Earth?
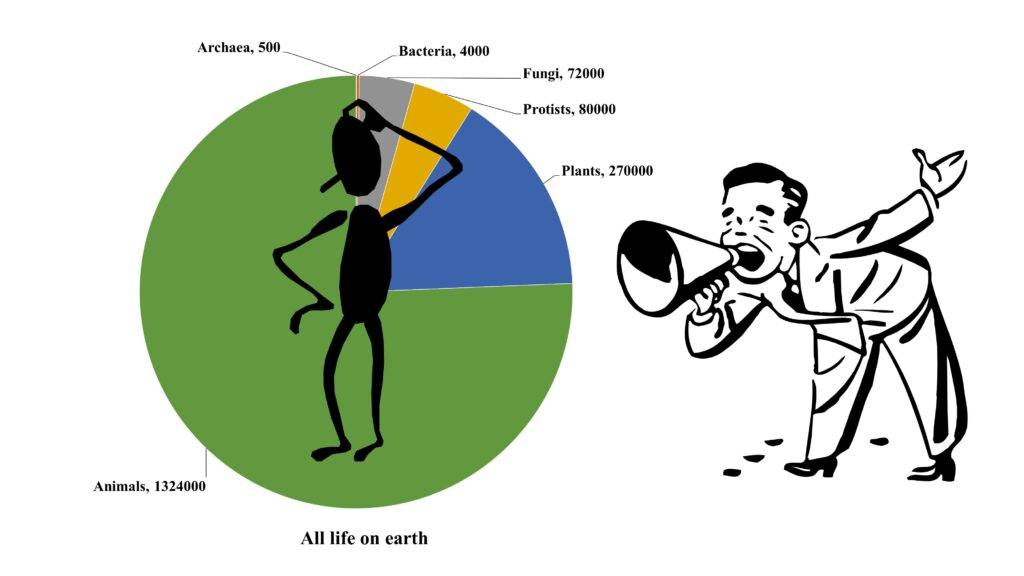
Wrap your head around this: the variety of life on Earth is like a super complicated puzzle. It includes all kinds of living things, like animals, plants, and even the tiny building blocks that make them unique. Now, putting a number on this diversity is like trying to count all the jellybeans in a giant jar-it’s not an easy task.
Here’s the deal: there are so many different species running around, and just when you think you’ve got them all, surprise! We find new ones, making the whole counting game a real challenge. And guess what? We humans aren’t making it any easier. Our habits of messing with habitats and polluting the place are like throwing obstacles in the path of biodiversity detectives.
Now, check this out: scientists take a wild guess that there might be around 8.75 million species having a party on Earth. But wait, that’s just a guess! The actual number is like a mystery waiting to be solved. Scientists have only given names to about 2.16 million of these species. That’s less than a quarter of the whole biodiversity gang!
But here’s the kicker: these numbers are like a growing game. We’re constantly uncovering new species, like finding hidden treasures in unexplored places, such as the deep sea, rainforests, and faraway habitats. Most of Earth’s diversity is still undercover, waiting for us to shine a spotlight on it.
So, next time you’re out exploring, remember that you might be stepping into a world where most of the residents are still incognito!
2. Why scientific forecasts of weather events are inaccurate?

Navigating the intricate world of weather forecasting is like trying to predict a dance where every move is influenced by countless factors. Despite our best efforts, present scientific weather forecasts, often reliant on complex models and observations, can hit a few wrong notes. Let’s unveil the mysteries behind this unpredictability and the possible reasons for the same.
1. Chaotic Atmosphere
The atmosphere is a chaotic playground where even tiny differences in the starting conditions can lead to major changes in weather patterns over time. This sensitivity, famously known as the butterfly effect, turns long-term predictions into a real head-scratcher.
2. Data Challenges
Present weather forecast models hunger for a feast of data such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and pressure. But if there are gaps or hiccups in this data buffet, it’s like trying to cook without all the ingredients. Inaccuracies can sneak in, affecting the forecast’s accuracy.
3. Assumptions Matter
Weather forecast models build upon assumptions about how the atmosphere behaves. If these assumptions miss the mark or leave gaps, it’s akin to trying to solve a puzzle with missing pieces.
4. Complex Interactions
Picture weather systems as a complex orchestra of variables—jet streams, ocean currents, land features, and more. Understanding and modelling these interactions is like trying to conduct a symphony where the musicians don’t always follow the script. It’s an ongoing challenge.
5. Scale and Resolution Limitations
Weather models have their blind spots, especially when it comes to small-scale events like thunderstorms or tornadoes. The grid size of the model might overlook these localized phenomena, creating gaps in the forecast.
6. Rapidly Developing Events
Some weather dramas unfold in the blink of an eye-sudden thunderstorms or intense rainfall. Predicting these swift acts with precision is like trying to catch a quick-change artist in action. It’s a tricky task.
7. Remote Challenges
In far-off or less-populated areas, observations are like scarce puzzle pieces. Predicting the weather accurately in these regions becomes a challenge when the puzzle is missing some critical components.
8. Climate Change Uncertainties
The Earth’s climate is throwing some curveballs, thanks to global warming. Changes in weather patterns introduce uncertainties, challenging forecasters to adapt to a shifting dance routine where historical data may no longer be a reliable partner.
In this intricate dance of atmospheric elements, accurate predictions remain a captivating challenge, reminding us that nature loves to keep us on our toes. Although, weather forecasts may not always be perfect, but they still provide valuable information that helps us prepare for and respond to various weather conditions.
3. Why can’t we measure and appraise the cost of ecosystem services?

Measuring and appraising the cost of ecosystem services is not possible as of now due to their intricate interdependencies, spatial and temporal variability, subjectivity, absence of market prices for many services, the presence of non-market goods, externalities, data limitations, and ethical concerns.
Ecosystem services often involve complex, interconnected ecological processes that resist straightforward quantification, and their values can vary widely by location, season, and individual perspective. Additionally, some services lack established market prices, making it hard to assess their economic worth, and their positive or negative impacts often extend beyond direct users, complicating cost estimation.
Despite these challenges, efforts to develop valuation techniques and incorporate ecosystem service values into decision-making continue, acknowledging the need to account for their significance in environmental and economic planning.
4. Why indigenous and traditional practices of environmental conservation are not protected?

Indigenous and traditional environmental conservation practices often lack protection. This is due to not being officially acknowledged, threats to land rights, inadequate legal safeguards, economic pressures, and cultural displacement. These practices, based on generations of wisdom, may not align with modern scientific views, and the communities may lack representation in decision-making processes. Efforts are underway to recognize and respect their rights, integrate their methods into conservation efforts, and promote legislation to safeguard their practices, as combining traditional knowledge with modern approaches can lead to more effective environmental protection.
Presently, a significant loss of valuable indigenous knowledge has occurred, and the reasons behind our failure to protect it remain perplexing. Therefore, this question has been included in the top 15 unanswered environmental questions.
5. Why current environmental awareness programs are ineffective?

Current environmental awareness programs are not as effective as intended and can’t be answered why this is so. However, there are a few factors which might be responsible for ineffectiveness. For example, information overload, the complexity of environmental issues, lack of personal relevance, the framing of messages, cultural and political divisions, the absence of tangible solutions, short-term focus, the challenge of behaviour change, resource limitations, and a lack of accountability.
To improve their efficacy, these programs must provide clear, actionable information, link environmental issues to individuals’ daily lives, adopt positive and solution-oriented messaging, address cultural and political sensitivities, and support long-term, well-funded strategies with measurable outcomes, ultimately encouraging meaningful environmental change. It can be noted that the key to all environmental progress and development is public awareness.
6. What are the true reasons for climate change?

Let’s break down the climate change story—it’s like a mix of nature’s hand and a bit of human mischief. While natural factors, like volcanoes and solar changes, have played climate games throughout Earth’s history, the current climate craziness is mostly our fault.
1. Natural and Human-Made Players
Climate change has a natural side, with things like volcanoes and solar shifts shaking things up. But hold on! Humans have entered the scene with a bang, and our activities are the main plot twist.
2. Historical Climate Swings
Earth’s climate has had its wild moments, thanks to natural tag-teams like volcanic eruptions and El Niño dances. These factors have taken turns influencing the weather over the ages.
3. Unprecedented Heat Wave
Here’s the headline news: the Earth’s temperature is skyrocketing, and it’s not a natural tantrum. The rapid rise in global temperatures over the past century is like a red flag, and we’re the ones waving it.
4. Greenhouse Gas Trouble
Enter the bad guys-greenhouse gases. Human activities, like burning fossil fuels and chopping down forests, are unleashing these troublemakers into the atmosphere. They trap heat like a warm blanket, turning up the planet’s thermostat.
5. IPCC’s Verdict
The IPCC, a group of climate whizzes, has spoken up. They’re 95-100% sure that more than half of the recent temperature jump (1951-2010) is on us. It’s like pointing fingers at our smokestacks and exhaust pipes.
6. Human Dominance Confirmed
Whether you look at specific climate signs or peek at different regions, the evidence shouts, “Humans did it!” We’re not just a part of the climate story; we’re the main characters causing the plot twists.
So, there you have it—climate change, a tale of both natural factors and human antics. But right now, we’re the ones holding the pen, and the story’s getting hotter by the chapter.
7. What is the ultimate fate of plastic pollution?

The ultimate fate of plastic pollution is a complex and concerning issue. Plastics, particularly single-use and non-biodegradable plastics, can persist in the environment for centuries. As plastic waste is discarded, it often ends up in landfills, littering terrestrial environments, and accumulating in the world’s oceans and waterways. In the environment, plastic waste can break down into smaller particles by photodegradation and mechanical weathering. This process can result in microplastics that can be ingested by marine life and potentially enter the food chain. The long-term consequences of microplastic in ecosystems and the potential effects on human health remain areas of active research. As per the present estimation sooner microplastic time bombs will destroy naturalness.
Efforts to address plastic pollution include reducing, recycling and waste management, and promoting the use of biodegradable and eco-friendly alternatives. However, it remains a significant global environmental challenge that requires ongoing attention and action to mitigate its long-term impacts.
8. Why is it challenging to control environmental infodemics?

The increasing environmental infodemic is undermining sustainability. Therefore it is important to regulate it as earliest as possible. However, controlling environmental infodemics is challenging due to the overwhelming volume and rapid spread of information. This is because of political and ideological polarization, the lack of traditional gatekeepers, and the algorithmic amplification of sensational content. In addition, cognitive biases that reinforce preconceptions, varied motivations, and the potential for misinformation to have far-reaching global consequences.
Addressing this challenge requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing media literacy education, and fact-checking efforts. Moreover, responsible social media practices, and public awareness campaigns in curbing the dissemination of false information. Therefore, this question has been included in the top 15 unanswered environmental questions.
9. What role do humans play on planet Earth?

The purpose of human beings on the planet is not well understood due to its complex and multifaceted role. Humans are both stewards and agents of change in the environment. As stewards, humans can conserve and protect ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources. They have developed sustainable practices and technologies that benefit the planet and its inhabitants. However, as agents of change, human activities have also led to significant environmental alterations. They have caused deforestation, habitat destruction, pollution, and the release of greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and biodiversity loss.
The challenge is to balance stewardship with responsible, sustainable choices for a harmonious coexistence with Earth. Moreover, the purpose of human beings on the planet needs to be explored further. Hence, this query has secured its place among the 15 most pressing unanswered environmental questions.
10. How do pollutants affect consciousness?

Let’s delve into the world of pollutants and their potential influence on our consciousness. Imagine heavy metals, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and airborne toxins as uninvited guests wreaking havoc in our central nervous system. Exposure to these troublemakers creates a symphony of neurological and cognitive symptoms, leaving us with impaired cognitive function, a memory playing hide-and-seek, and mood swings that might lead to conditions like “brain fog,” fatigue, and irritability. The long-term effects are even more intriguing, as constant exposure can gradually shape not just our cognitive function but also our emotional state, like a subtle dance with our mental well-being.
However, understanding the specific impact of pollutants on consciousness is akin to solving a puzzle missing some critical pieces. The uncertainty stems from the type and level of exposure and individual susceptibility, making it a complex area of study. Imagine trying to decode a language where pollutants hold the key, and the effects on our minds remain a head-scratcher due to the intricate interplay of these factors. It’s a tangled web that scientists are working to unravel, shedding light on the mysterious ways pollutants might be affecting our mental landscape.
It’s important to note that the specific effects of pollutants on consciousness are uncertain. This is possibly due to the type and level of exposure, and individual susceptibility making it a complex area of study.
11. Why Earth’s magnetic poles are shifting rapidly?
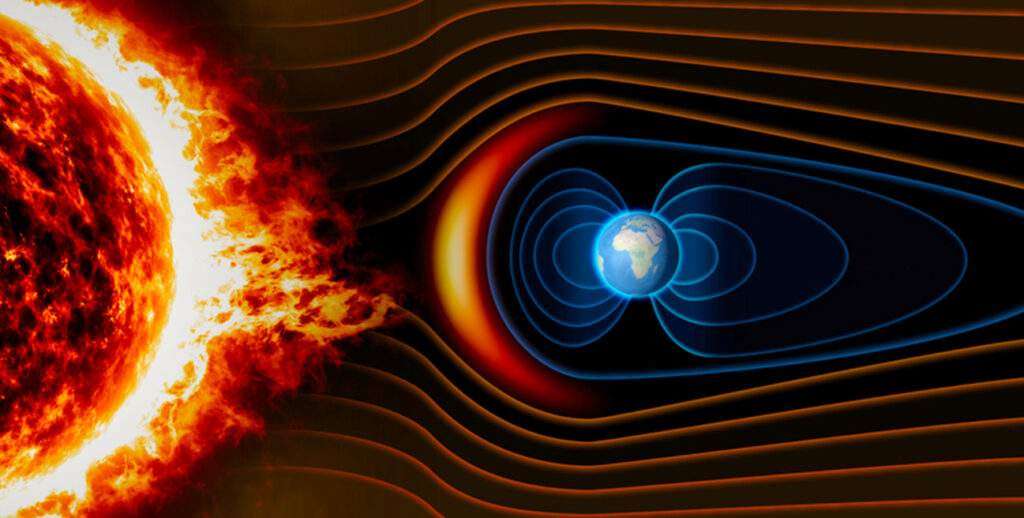
The Earth’s magnetic poles are shifting, primarily due to complex processes occurring in the planet’s molten outer core. Earth’s magnetic field is generated by the motion of molten iron and nickel in the outer core. But why this field is variable and rapidly changing over time?
The rapid shift in the magnetic poles is possibly due to the dynamic nature of the molten core. Small-scale movements and turbulence in the core, known as geomagnetic jerks, can influence the larger-scale behaviour of the magnetic field.
At present, the North Magnetic Pole is moving from northern Canada towards Siberia at an accelerating rate. However, it’s still a gradual and appears to be a natural geological process.
The shifting magnetic poles have implications for navigation, especially for compass use and certain technologies. As per the prediction, the change in the earth’s magnetic field can have the potential to end the existence of life on our planet. Scientists continue to monitor these changes to better understand their underlying mechanisms and their potential impacts. Hence, this query has earned its place among the foremost 15 unanswered environmental questions.
12. Does life exist beyond planet Earth?

The existence of life beyond Earth remains an unanswered question, with ongoing exploration efforts focusing on places like Mars, icy moons, and exoplanets in the habitable zone. Earth’s extremophiles show life can adapt to extreme conditions, while the search for extraterrestrial intelligence seeks signals from advanced civilizations.
The Fermi Paradox underlines the challenges of detecting extraterrestrial life, given the vastness of the universe. Our definition of life may limit our ability to recognize it elsewhere, but the quest to find life beyond Earth continues through scientific exploration and technological advancements.
13. What is the actual process responsible for the origin of life on Earth?

Unravelling the mystery of how life first kicked off on Earth is like peeling away layers of an ancient puzzle, and scientists are still deep in the investigation. One leading idea suggests that life might have sparked from a mix of complex chemical reactions, playing out in a sort of primordial soup near hydrothermal vents beneath the ocean. Picture it like a bustling kitchen where these reactions cooked up self-replicating molecules, laying the groundwork for the grand show of cellular life.
Backing up this notion are experiments in the lab and our understanding of chemistry, painting a compelling picture of life’s possible origin story. Yet, the exact details and the play-by-play mechanisms of this ancient drama are still veiled in mystery, keeping researchers on their toes in the quest for answers. So, while this hypothesis holds weight, the origin of life on Earth continues to be one of the captivating enigmas that science is eager to crack.
14. What were the reasons behind the decline of the impressive Polynesian civilization on Easter Island?
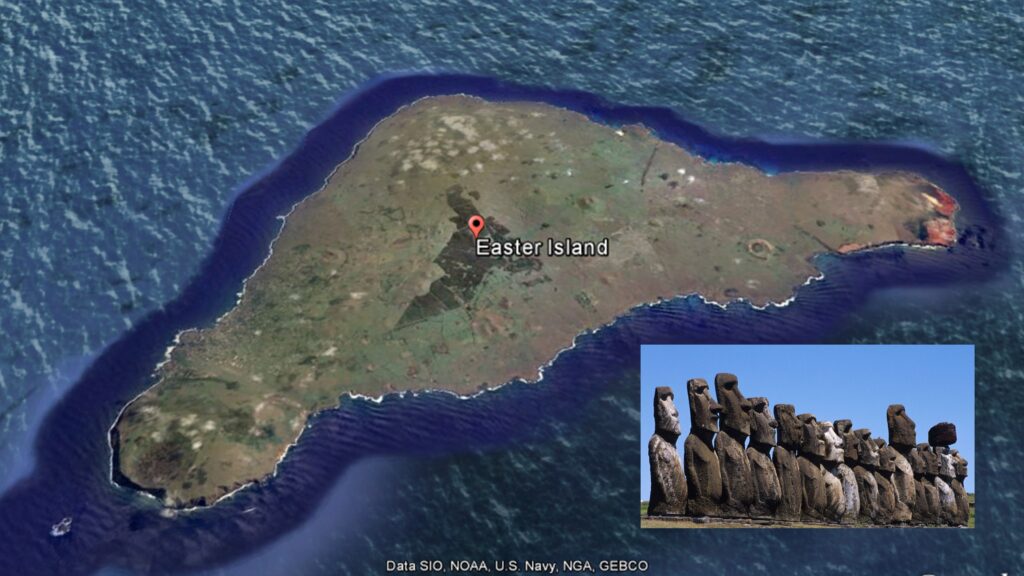
The decline of the Polynesian civilization can be attributed to a combination of environmental, social, and cultural factors. The island’s deforestation, largely driven by the islanders for agriculture, transportation, and the construction of massive stone statues (moai), led to soil degradation and reduced agricultural productivity. As resources dwindled, competition for the remaining resources and societal strife grew. This environmental degradation and social unrest likely contributed to the decline of the civilization.
The missing link in this story is the critical point at which the islanders’ society, reliant on a limited environment, failed to adapt to the changing conditions and resource depletion. This led to societal collapse, deforestation, and the erosion of the culture that once thrived on Easter Island. The exact details of how and why this happened remain a subject of ongoing research and debate.
15. Do exoplanets affect human health and the environment?

The impacts of exoplanets on human health and the environment have not been studied so far. Since exoplanets are currently beyond our technological reach and remain unexplored.
The discovery of habitable exoplanets could have indirect implications for astrobiology and our understanding of planetary environments. Therefore, the potential impact on human health and the environment resulting from future exploration or interaction with exoplanets remains a theoretical consideration as of now. Hence, this query has secured its place among the 15 most pressing unanswered environmental questions.

