
Public health is a multifaceted field requiring diverse expertise to tackle today’s challenges, including infectious diseases, chronic illnesses, environmental hazards, and social determinants. Interdisciplinary science plays a crucial role by fostering collaboration among experts from fields like medicine, epidemiology, psychology, economics, social sciences, humanities, geography, and law to address complex public health issues comprehensively. 6 important links between interdisciplinary science and public health are as follow:
1. Help to understand complex and multifaceted problems
Public health problems are often complex and multifaceted, involving a range of factors that interact with each other in complex ways. By bringing experts together from different fields, we can gain a better understanding of the complex factors that contribute to preventable diseases. For example, reducing tobacco use requires understanding not only the health effects of smoking, but also the psychological, sociological, economic, cultural, and policy factors that influence smoking behavior. Only by bringing together experts from different fields can we develop a comprehensive understanding of these factors and develop effective interventions.

2. Help to develop effective interventions and policies
Interdisciplinary research can lead to more effective interventions and policies. By drawing on a range of expertise, interdisciplinary research can develop interventions that are more tailored to the needs of specific populations and that take into account the many factors that influence health outcomes. This can lead to more effective interventions that are more likely to be adopted by communities and that have a greater impact on public health.
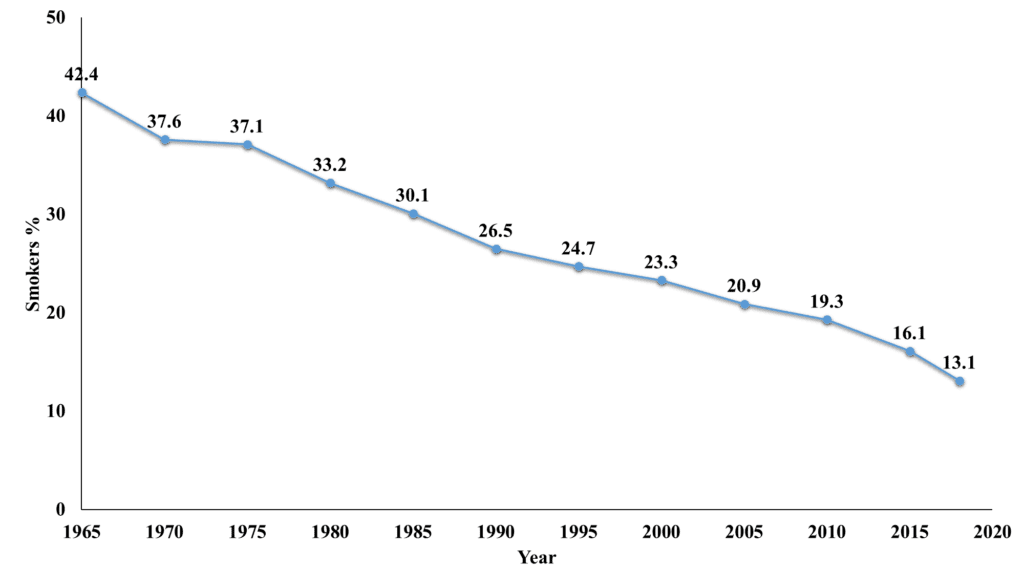
Behavioural and social sciences research has driven a dramatic decline in smoking rates, saving lives and reducing diseases. This success, achieved through policies like smoking bans and taxes, stands as a remarkable public health achievement. Despite nicotine’s addictive nature, this research has helped people quit smoking, improving society’s well-being.
Over the past decade, there has been a notable reduction in overall cancer death rates. This is primarily due to a substantial decrease in smoking rates, which have dropped from 42.6% in 1965 to 13.7% in 2018.
3. Help to implement research for better health
Interdisciplinary approaches offer a holistic understanding of health problems by considering biological, social, psychological, and environmental factors. Collaboration among diverse experts leads to innovative solutions, such as advanced medical devices and treatments. Interdisciplinary teams help in the following key task to translate research into problem-based practical solutions.
- Find out why problems happen and create plans to stop them.
- Combine data from different places to learn more.
- Help make rules and plans based on facts.
- Decide where to use resources best.
- Talk to communities and work with them.
- Deal with big health problems worldwide.
- Put patients at the centre and make healthcare better.
In addition, It helps to bridge the gap between research and practice. By involving practitioners and policymakers in the research can ensure that findings are more likely to be translated into practice and that policies are more likely to be evidence-based.
4. Help in the effective monitoring of health status
Advances in technology are making it possible to achieve population health-behaviour changes. For example, wearable devices can help people track their physical activity and monitor their health. Social media platforms can also be used to promote healthy behaviours and connect people with resources.
Moreover, Interdisciplinary teams excel at integrating data from various sources. This allows for a more nuanced understanding of health trends and correlations that may not be apparent when examining data in isolation. Moreover, by combining expertise in epidemiology, environmental science, and data analysis, can develop early warning systems for disease outbreaks or health crises. This proactive approach helps in timely response and mitigation.
5. Help to build One Health Surveillance Systems
Interdisciplinary science plays a pivotal role in building effective One Health Surveillance Systems. It aims to monitor and address health threats at the intersection of human, animal, and environmental health. This approach is needed to address the complex factors that contribute to preventable diseases. Further, this approach involves interconnections between different factors, such as social determinants of health, environmental factors, and individual behaviours.
Read more about One Health Surveillance Systems

6. Help to connect with others
Interdisciplinary science not only advances knowledge but also fosters connections and collaborations among individuals and groups. The shared purpose brings together experts from diverse fields who are united by a common goal, creating a sense of community and collaboration. Social connections are important for overall health and well-being. Therefore, make time for friends and family, and consider joining a community group or club. By taking these steps, you can improve your health and contribute to the overall health of your community. Remember, small changes can make a big difference!
Conclusion
Interdisciplinary science is a critical component of public health research and practice. Bringing together experts from different fields helps to develop a comprehensive understanding of public health problems. Further, it helps to develop more effective interventions and policies and bridge the gap between research and practice. As we continue to face new and complex public health challenges, an interdisciplinary approach will be more important than ever.

