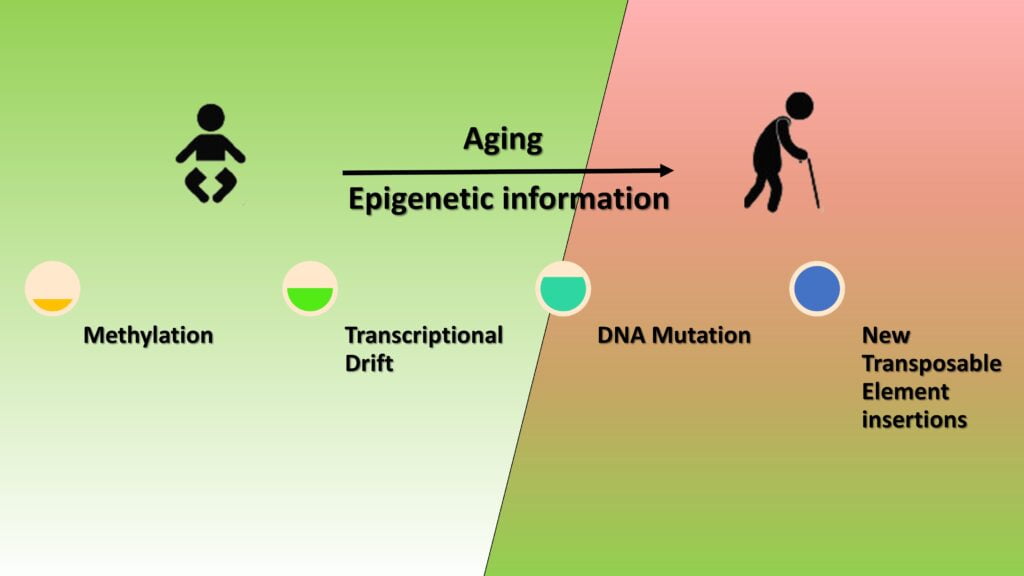
As we grow, our cells undergo changes that affect our genes work. Recent discoveries show that the patterns of gene changes are highly variable among people. However, some epigenetic changes are common. For example, divergent DNA methylation with age, loss of heterochromatin and alteration of histone modifications. These changes are highly affected by endogenic and exogenic factors such as diet, exercise, stress and surrounding environmental conditions. Therefore, ageing can not be stopped due to endogenetic factors. However, it can be slowed down by controlling exogenic factors that influence our epigenetics. Based on scientific discovery, the top 20 ways to prevent epigenetic changes and slow down ageing are as follows:
1. Healthy Diet

Diet is an important factor that can affect epigenetic age. A healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains has been shown to have a positive impact on epigenetic age. On the other hand, a diet that is high in processed foods and sugar can lead to epigenetic changes that accelerate ageing. Based on a recent study, a better and balanced diet quality can reduce the epigenetic age by 0.8–1.5 years. Therefore, a balanced diet based on the requirements of the body and activities is crucial to prevent epigenetic changes and slow down ageing.
2. Regular Exercise

Exercise is also important for maintaining a healthy epigenetic age. Regular exercise has a positive impact on DNA methylation, which can help to slow down the ageing process. Studies have shown that exercise can even reverse some epigenetic changes with age. Based on a scientific study, women who exercise more than 2.5 hours per week can significantly slow down the ageing process. Therefore, regular exercise along with the proper required diet can significantly prevent epigenetic changes and slow down the ageing process.
3. Stay Hydrated

Water itself does not directly influence the chemical modifications to DNA and slow the ageing process. However, adequate water intake is crucial for cellular function, supporting nutrient transport and waste elimination. It aids in natural detoxification. Moreover, hydration is key for skin health, preventing dryness and maintaining a youthful appearance. It also supports joint lubrication, reducing stiffness and promoting overall joint health. Additionally, staying well-hydrated is essential for optimal cognitive function, potentially reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
4. Regular Consumption of Adaptogen Herbs

Adaptogen herbs such as turmeric, ashwagandha, rhodiola, holy basil and green tea can help to adapt to stress conditions and restore homeostasis. For example, turmeric which contains curcumin has natural antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which help to prevent or slow down epigenetic changes. Therefore, regular consumption of turmeric along with regular physical exercise can potentially slow down the ageing process. Additionally, curcumin has neuroprotective effects and may help to prevent or treat brain diseases. Moreover, curcumin prevents cancer progression by inhibiting telomerase activity and potentially slowing the ageing process.
5. Maintain BMI

Elevated BMI is linked to increased inflammation, osteoarthritis and cardiovascular diseases. In addition, higher BMI accelerates telomere shortening leading to cellular ageing and influencing hormonal balance. A healthy BMI (18.5 to 24.9) maintained through lifestyle choices can prevent epigenetic changes and slow down the ageing process. As per the scientific study, 10 units of BMI (10 Kg/m2) correspond to 1-3 years of epigenetic age.
6. Manage Stress

Stress is a common factor that can affect epigenetic age. Studies have shown that chronic stress can lead to changes in DNA methylation, a type of epigenetic modification affecting gene expression. This can lead to accelerated ageing and an increased risk of age-related diseases such as cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, chronic stress can contribute to ageing and age-related diseases. So managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can be beneficial to slow down ageing and reverse epigenetic changes.
7. Caloric Restriction Mimetics (CRMs) in Nutrition

Caloric restriction mimetics (CRMs) mimic the effects of caloric restriction on the body. For example, Polyamines (e.g. spermidine), Polyphenols (e.g. resveratrol, curcumin, and quercetin), NAD+ precursors, Salicylic acid and Glycolytic inhibitors (e.g. D-allulose and D-glucosamine). These CRMs activate pathways associated with caloric restriction, such as autophagy and stress response. It also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, contributing to their potential health benefits. Reducing caloric intake by 25% for two years reduces the pace of ageing by 2–3%.
8. Include Senolytic Agents

Senolytic agents can target and get rid of old cells (senescent cells). These cells have stopped dividing and are linked to getting older and age-related diseases. When these senolytic agents are used, these old cells go through a natural process called apoptosis (self-destruction). Removing these old cells makes tissues work better, reduces swelling and slows down the ageing process.
For example, fisetin found in strawberries can help to remove ageing cells through apoptosis. Studies suggest that it has a positive impact on health and can contribute to preventing epigenetic changes and slowing down ageing.
9. Regular Meditation

Regular meditation slows the ageing process by reducing stress and inflammation as well as it promotes antioxidant activity. Chronic stress increases inflammation and oxidative stress, damaging DNA, and gene expression, and accelerating ageing. In addition, meditation can increase telomerase activity, an enzyme that helps maintain telomere length and prevent ageing. Therefore, regular meditation with a healthy diet can significantly reduce the pace of ageing. As per the recent data, each year of practice can reduce the epigenetic age by an average of 0.24 years.
10. Adequate sleep

Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and mitigating age-related cognitive decline. During sound sleep, the body repairs cells and releases growth hormones, promoting skin health. It plays a vital role in collagen production, preventing wrinkles and maintaining a youthful complexion. Sleep regulates inflammation, hormonal balance and antioxidant defence, countering the ageing process. Moreover, sound sleep can improve blood circulation which enhances skin health, supports memory consolidation and optimal cognitive function.
11. Social engagement

Maintaining social connections and engaging in meaningful activities can help to promote mental and emotional well-being, which is important for healthy ageing. Studies show that being around friends can help you think better and slower. It also makes you less stressed, less likely to feel sad, and keeps your body healthy. So, having good friends and spending time with them can make you feel younger and healthier for a longer time.
12. Avoiding harmful substances

Limiting alcohol consumption, avoiding smoking, and reducing exposure to environmental toxins can help to promote healthy ageing. For example, smoking can introduce chemicals such as benzene, arsenic and formaldehyde into your body that can harm your skin and make you look older. When you avoid smoking and other harmful stuff, your body doesn’t have to work hard to fix the damage. It’s like letting your body stay young and healthy. Harmful substances can also make you sick, and being sick can make you age faster too. So, by staying away from things like smoking and alcohol you’re giving your body a better chance to stay young and keep you feeling good.
13. Include Supplementation

Additional nutrients such as vitamins, Omega-3 fatty acids and required minerals can bridge potential gaps in our diet for optimal health and longevity. For example, vitamin C required for skin strength is often insufficient in our diet; here, a supplement can serve as a beneficial addition. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil supplements offer support for brain and heart health. Supplements act as a strategic backup plan, ensuring that the body receives essential nutrients, contributing to overall well-being and acting as a preventive measure against premature ageing.
Therefore, a daily multivitamin containing key nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E, along with minerals like zinc and selenium, can enhance the body’s antioxidant defence, protecting against cellular damage associated with ageing.
14. Daily Sunlight Exposure

Sunlight exposure is crucial for the synthesis of collagen and vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and immune function. In addition, it helps to regulate the body’s circadian rhythm. A well-regulated circadian rhythm is associated with better sleep quality.
However, it’s important to note that excessive or unprotected sunlight exposure can damage the collagen and elastin fibres (photoaging), characterized by the premature development of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. Moreover, prolonged exposure to UV radiation can cause DNA damage in skin cells, increasing the risk of skin cancers and contributing to ageing.
Therefore, adequate levels of sunlight especially in the morning can contribute to healthy ageing by supporting bone density, reducing the risk of fractures, and maintaining a well-functioning immune system.
15. Clean and Green Space

A healthy environment reduces exposure to pollutants and toxins that can accelerate the ageing process and induce epigenetic modifications. For instance, air and water pollution can induce oxidative stress and inflammation. Whereas, a green environment with abundant vegetation helps to improve air quality by absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen. Studies have shown a positive correlation between green space and mental health.
The reduced exposure to environmental stressors in a clean environment can also have positive effects on the epigenome. Stress and exposure to pollutants are linked to changes in DNA methylation and histone modification patterns. Therefore, a clean and green space can significantly prevent epigenetic changes and slow down ageing.
Follow 11 Essential Strategies to maintain clean and green space to minimize the effects of exogenic ageing factors.
16. Consumption of Natural Extremolytes

Extremolytes are natural molecules made by microorganisms thriving in extreme environments like high and low temperatures, high salinity, and deep regions. These organisms produce molecules such as canthaxanthin, ectoine, pipecolic acid, hydroxy ectoine, mannosyl-glycerate, mannosyl-gylceramide, glucosyl-glycerate, glucosyl-glycerol, etc which exhibit protective effects. For example, Bradyrhizobium sp. and Haloferax alexandrines produce canthaxanthin, which is used to colour food and beverages, as well as salmon flesh. In addition to bacteria, microalgae are also used to extract carotenoids for dietary supplements. Astaxanthin, obtained from microalgae H. pluvialis and extremophiles from the red snow in Antarctica, is used as a supplement in diets for both humans and animals.
17. Intermittent Fasting

Intermittent fasting can keep our cells healthy by removing damaged parts through the autophagy process, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. In addition, intermittent fasting activates Sirtuins (protein) which play an important role in maintaining the integrity of the genome and repairing DNA.
Therefore, a cycle of eating and fasting can significantly slow down the ageing process and reverse epigenetic changes. At the same time, make sure your body is well hydrated and the required minerals are supplied through mineral water.
To plan intermittent fasting, you may listen to your body and pay attention to your hunger and the requirements of the body. Remember, longer fasting will promote fat storage in response to starvation and lead to more complications.
18. Practice Good Oral Hygiene

Poor oral hygiene causes chronic inflammation and is responsible for various age-related conditions, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Chronic inflammation may also contribute to epigenetic changes, altering gene expression patterns. Additionally, microbiota associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream, potentially affecting distant organs and tissues. Therefore, regular brushing and flossing can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and associated inflammation. This, in turn, may contribute to overall health, potentially influencing the ageing process and minimizing epigenetic alterations associated with systemic inflammation.
19. Limit Sugar and Processed Foods

Excessive sugar consumption can lead to the formation of reactive oxygen species which create oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can significantly damage DNA and lead to ageing faster. Whereas, processed foods often contain high levels of refined carbohydrates, unhealthy fats, and additives. These compounds can trigger inflammation and lead to ageing faster. Moreover, diets high in refined carbohydrates can lead to insulin resistance which promotes the ageing process.
By adopting a diet that limits sugar and processed foods we can significantly slow down the ageing process by mitigating oxidative stress, modulating inflammation, and improving insulin sensitivity.
20. Choose Healthy Fats
Healthy fats such as unsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids are essential to maintain the integrity of cell membranes and cellular communication. These fats are naturally available in olive oil, avocados, nuts, salmon and flaxseeds. For example, olive oil and avocados contain monounsaturated fats which help to reduce chronic inflammation associated with aging. On the other hand, nuts and seeds contain antioxidants that combat oxidative stress. Whereas, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) from fatty fish and algae is crucial for brain health and supports cognitive function. Moreover, healthy fats play a major role in hormonal balance and significantly slow down the ageing process.
Conclusion
Environmental factors such as stress, diet and exercise can have a significant impact on our epigenetic age. By managing these factors, we can slow the ageing process and maintain a healthy biological clock. Following the proper strategies and staying informed about the latest research as discussed earlier can slow down ageing. Remember the ageing process is variable among the people and group. Therefore, personalizing strategies with the help of healthcare professionals or nutritionists based on individual needs can provide the best result.
Remember, understanding your ageing factors and wisely acting on them is the key to managing and reducing the ageing process. In addition, you may calculate personal life expectancy and optimise it to slow down ageing and prevent epigenetic changes.

