COMPETITIVE EXAM MCQs SERIES of ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE for UGC-NET/JRF, SLET, ARS, GATE, and other entrance tests – Environmental Pollution and Control: – Air Pollution and Control.
Syllabus Outline
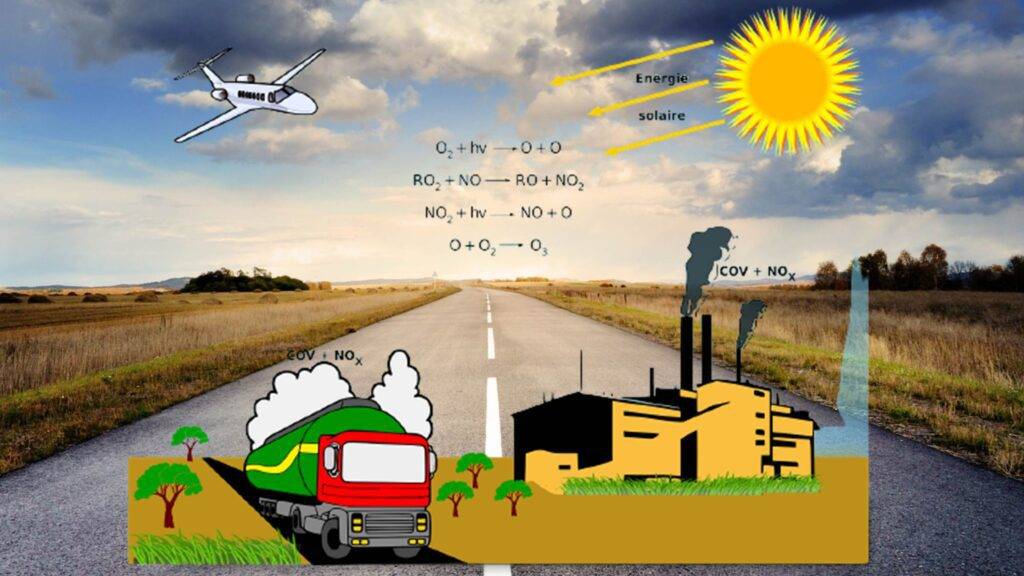
- Introduction to air pollution (e.g. definition, sources, classification of pollutants, and associated health and environmental impacts).
- Emission sources and dispersion mechanisms of major air pollutants (e.g. particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, ozone, and heavy metals).
- Monitoring and measurement techniques, air quality standards, and relevant legislation.
- Health effects of air pollution.
- Air pollution control technologies.
- Indoor air quality, risk assessment, and urban air pollution.
This quiz contains the concept-based most frequently asked 25 MCQs of “Environmental Pollution and Control – Air Pollution and Control“. Each question has a single correct/most appropriate answer.
*****
1. Which of the following is NOT considered a primary air pollutant?
a) Nitrogen dioxide
b) Carbon monoxide
c) Sulfur dioxide
d) Ozone
2. The process of photochemical smog formation involves the reaction of:
a) Nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide
b) Volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides
c) Ozone and sulfur dioxide
d) Carbon monoxide and particulate matter
3. Which pollutant is mainly responsible for acid rain?
a) Sulfur dioxide
b) Carbon monoxide
c) Lead
d) Particulate matter
4. The temperature inversion exacerbates air pollution because of it:
a) Traps pollutants close to the ground
b) Accelerates the dispersion of pollutants
c) Increases the efficiency of pollutant removal by precipitation
d) Reduces the production of secondary pollutants
5. Catalytic converters in automobiles primarily function to reduce emissions of:
a) Nitrogen oxides
b) Carbon monoxide
c) Hydrocarbons
d) Particulate matter
6. The process of scrubbing in air pollution control involves the removal of pollutants through:
a) Absorption into a liquid or solid
b) Adsorption onto a surface
c) Precipitation as solid particles
d) Thermal decomposition
7. The main purpose of a baghouse filter in air pollution control is to remove:
a) Gaseous pollutants
b) Particulate matter
c) VOCs
d) Radioactive substances
8. Which pollutant is NOT primarily emitted from vehicle exhaust?
a) Nitrogen dioxide
b) Carbon monoxide
c) Particulate matter
d) Sulfur dioxide
9. The concept of residence time in the atmosphere refers to:
a) Time taken for a pollutant to be absorbed into the atmosphere
b) Time taken for a pollutant to react with other substances in the atmosphere
c) Time taken for a pollutant to be removed from the atmosphere by physical processes
d) Time taken for a pollutant to reach its maximum concentration in the atmosphere
10. Which pollutant contributes primarily to smog formation in urban areas?
a) Carbon dioxide
b) Methane
c) Ozone
d) Hydrogen sulfide
11. The Montreal Protocol primarily addresses the global phase-out of:
a) Lead-based gasoline
b) Nitrogen oxides
c) Chlorofluorocarbons
d) Particulate matter emissions
12. The term fugitive emissions refers to:
a) Emissions from stationary sources
b) Emissions from mobile sources
c) Unintentional releases of pollutants from various sources
d) Controlled releases of pollutants during industrial processes
13. Which pollutant contributes primarily to black carbon formation?
a) Sulfur dioxide
b) Carbon monoxide
c) Nitrogen oxides
d) Particulate matter
14. The Kyoto Protocol primarily focuses on reducing emissions of:
a) Sulfur dioxide
b) Carbon monoxide
c) Greenhouse gases
d) Nitrogen oxides
15. Which of the following pollutants is a greenhouse gas with a significantly higher warming potential than carbon dioxide?
a) Methane
b) Ozone
c) Sulfur dioxide
d) Nitrogen dioxide
16. The London smog of 1952 was primarily caused by the combustion of:
a) Coal
b) Natural gas
c) Diesel
d) Gasoline
17. Which pollutant is primarily responsible for brown haze over urban areas?
a) Carbon monoxide
b) Ozone
c) Nitrogen dioxide
d) Particulate matter
18. Which of the following pollutants is primarily responsible for industrial smog?
a) Carbon monoxide
b) Nitrogen oxides
c) Sulfur dioxide
d) Particulate matter
19. The concept of emission trading involves:
a) Exchanging emission reduction credits between industries
b) Trading emissions between different countries
c) Banning the emission of certain pollutants
d) Taxing emissions based on their environmental impact
20. The primary source of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in urban environments is:
a) Volcanic eruptions
b) Biomass burning
c) Industrial processes
d) Vehicular emissions
21. A research study suggests a positive correlation between exposure to PM2.5 and cardiovascular diseases. This is likely due to:
a) Direct mechanical damage to lung tissue
b) Increased inflammation and oxidative stress
c) Reduced oxygen availability in the bloodstream
d) All of the above
22. A fluidized bed combustor offers an advantage over conventional combustion by:
a) Reducing emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx)
b) Increasing the efficiency of fuel-burning
c) Decreasing the formation of particulate matter
d) All of the above
23. Which of the following best describes the origin of brown carbon aerosols?
a) Combustion of fossil fuels like coal and oil
b) Secondary organic aerosol formation from volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
c) Direct emissions from soil dust
d) Erosion of weathered rocks
24. Which life cycle stage of electric vehicles contributes the MOST to air pollution?
a) Vehicle operation
b) Battery production
c) Vehicle disposal and recycling
d) Maintenance and repair activities
25. Which property is the main concern for CFC replacement?
a) High flammability
b) Low boiling point
c) High ozone depletion potential
d) Toxicity to aquatic organisms
*****
Previous: Exploitation of Renewable Energy Resources
Next: Sampling and Monitoring of Air Pollutants
References
- Seinfeld, John H., and Pandis, Spyros N. (2016) Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, John Wiley & Sons, 3rd edition.
- Singh, R. B., and Sinha, R. K. (2017) Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet, Khanna Publishers, 1st edition.
- Rao, M. N., and Rao, H. V. N. (2018) Air Pollution Control, McGraw Hill Education, 7th edition.
