COMPETITIVE EXAM MCQs SERIES of LIFE SCIENCES for CSIR-UGC NET/JRF, SLET, GATE, and other entrance tests – MOLECULES AND THEIR INTERACTION RELEVANT TO BIOLOGY – Bioenergetics and Energy Pathways.
Syllabus Outline
- Laws of thermodynamics in biological systems
- Gibbs free energy and coupled reactions
- High-energy compounds – ATP, GTP, phosphoenolpyruvate
- Group transfer reactions (phosphoryl, acyl, methyl)
- Overview of glycolysis and its regulation
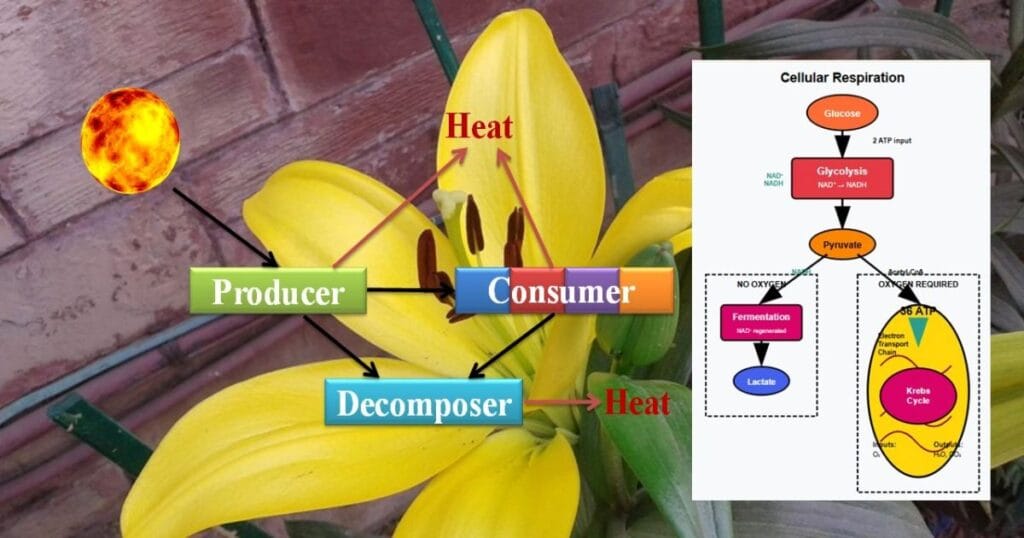
- TCA cycle – intermediates and energy yield
- Oxidative phosphorylation – electron transport chain, ATP synthase
- Chemiosmotic theory and proton motive force
- Redox reactions and coenzymes (NAD+/NADH, FAD/FADH2)
- Biological energy transducers – mitochondria and chloroplasts
This quiz contains concept-based, most frequently asked 25 MCQs of “MOLECULES AND THEIR INTERACTION RELEVANT TO BIOLOGY – Bioenergetics and Energy Pathways”. Each question has a single correct/most appropriate answer.
*****
1. Under standard conditions, ATP hydrolysis has ΔG°′ ≈ −30.5 kJ mol⁻¹, but in vivo it is more negative (≈ −40 kJ mol⁻¹). What explains this difference?
A) High water concentration drives hydrolysis.
B) Cytoplasmic pH remains constant.
C) High ATP/ADP and Pi ratio in cells.
D) Coupling to endergonic reactions.
2. Assertion (A): Living systems maintain order by exporting entropy to their surroundings.
Reason (R): Organisms exist at chemical equilibrium.
A) Both A and R are true; R explains A.
B) Both true, but R doesn’t explain A.
C) A true; R false.
D) A false; R true.
3. What best explains the sigmoidal oxygen-binding curve of haemoglobin?
A) Single binding site and constant affinity.
B) Cooperative binding among subunits.
C) Covalent heme–O₂ bond formation.
D) Independent subunit binding.
4. The Henderson–Hasselbalch equation relates pH, pKa, and the ratio of acid/base as:
A) pH = pKa + log([HA]/[A⁻])
B) pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
C) pH = pKa × [A⁻]/[HA]
D) pH = pKa − log([A⁻]/[HA])
5. Which interaction stabilises α-helices and β-sheets?
A) Covalent bonds
B) Hydrogen bonds
C) Hydrophobic interactions
D) Ionic bonds
6. Competitive inhibition is characterised by:
A) Decreased Vmax only
B) Increased Km; Vmax unchanged
C) Decreased Km; Vmax unchanged
D) Both Km and Vmax decreased
7. Which process produces the largest ATP yield per glucose molecule?
A) Glycolysis
B) Citric acid cycle
C) Electron transport chain
D) Fermentation
8. Which molecule has the highest phosphoryl transfer potential?
A) ATP
B) Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
C) Glucose-6-phosphate
D) Creatine phosphate
9. The allosteric enzyme aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) is inhibited by:
A) ATP
B) CTP
C) UTP
D) AMP
10. Denaturation of proteins affects:
I – Primary Structure
II – Secondary Structure
III – Tertiary Structure
IV – Quaternary Structure
A) IV only
B) III and IV
C) II, III and IV
D) I, II, III and IV
11. Which of the following statements most accurately reflects the Second Law of Thermodynamics as it applies to a living organism?
A) The total energy of the organism and its surroundings remains constant throughout its lifetime.
B) Organisms maintain a highly ordered internal state by increasing the disorder (entropy) of their surroundings.
C) Energy is neither created nor destroyed, but converted from one form to another within the organism.
D) All spontaneous processes within the cell proceed toward a state of lower free energy.
12. The Glycerophosphate Shuttle is a mechanism that effectively transfers electrons from cytosolic NADH to the mitochondrial ETC. The net result of this shuttle in terms of electron carrier is:
A) Cytosolic NADH is transferred to mitochondrial NADH.
B) Cytosolic NADH is converted to mitochondrial FADH.
C) Cytosolic NAD+ is reduced to NADH in the mitochondrial matrix.
D) Cytosolic FADH is oxidised to FAD in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
13. In the TCA cycle, the enzyme Succinyl-CoA Synthetase catalyses the only substrate-level phosphorylation step. In animal cells, the GTP produced is primarily used for:
A) Directly driving Sodium-Potassium pumps across the plasma membrane.
B) Driving the hydrolysis of Acetyl-CoA to Acetate.
C) Transferring its terminal phosphate to ADP by Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase.
D) Directly regulating the activity of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase.
14. Which of the following is the final electron acceptor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain of aerobic organisms?
A) Water
B) Oxygen
C) Cytochrome
D) Ubiquinone
15. Chemiosmotic theory proposes that the energy for ATP synthesis comes from the Proton Motive Force (PMF). The main components contributing to PMF across the inner mitochondrial membrane are:
A) Chemical potential energy from the pH gradient and electrical potential energy from the membrane potential.
B) The ATP and ADP concentration gradient.
C) The heat produced by electron transfer and the mechanical force from ATP Synthase rotation.
D) The concentration of NAD+ and NADH.
16. Rotenone is a potent inhibitor of the Electron Transport Chain. Its addition to isolated mitochondria actively oxidising Pyruvate would specifically block:
A) The reduction of Oxygen to Water.
B) The transfer of electrons from Complex I to Ubiquinone.
C) The transfer of electrons from Complex II to Ubiquinone.
D) The transfer of electrons from Cytochrome C to Complex IV.
17. Dinitrophenol is an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation. The presence of Dinitrophenol in a suspension of isolated mitochondria will lead to:
A) Increased ATP synthesis and decreased rate of O2
B) Decreased ATP synthesis and increased rate of O2
C) Decreased ATP synthesis and decreased rate of O2
D) Unaffected ATP synthesis and decreased rate of O2
18. The major electron donors that directly feed electrons into the Ubiquinone pool in the mitochondrial ETC are:
I – NADH from Complex I
II – FADH2 from Complex II
III – NADH from Complex III
IV – Glycerol-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase
V – Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase
A) I, II, and III only
B) I, II, IV, and V only
C) II, IV, and V only
D) I, II, III, IV, and V
19. In a plant cell, the Calvin Cycle requires ATP and NADPH. These are generated in the Light Reactions of photosynthesis. The process by which ATP is synthesised in the Thylakoid membrane is known as:
A) Substrate-level phosphorylation
B) Peroxidative photophosphorylation
C) Oxidative phosphorylation
D) Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
20. A difference between the mitochondrial ETC and the Chloroplast electron transport system is:
I – Protons are pumped from the Matrix to the Intermembrane Space in Mitochondria, while in Chloroplasts, they are pumped from the Stroma to the Thylakoid Lumen.
II – Cytochrome c is an electron carrier in the Chloroplast but not in the Mitochondrion.
III – Water is the electron donor in Mitochondria, whereas NADH is the electron donor in Chloroplasts.
IV – ATP synthesis is coupled to electron transport in Mitochondria but not in Chloroplasts.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) I, II, III and IV
21. Which of the following high-energy phosphate compounds is primarily involved in the synthesis of Peptide Bonds during Translation?
A) ATP
B) UTP
C) CTP
D) GTP
22. In Skeletal Muscle under intense exercise, Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is generated. This molecule acts as a powerful allosteric regulator by:
A) Activate transport of ADP into the mitochondrial matrix to release instant energy.
B) Activating Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase to activate gluconeogenesis.
C) Activating Phosphofructokinase-1 to stimulate glycolysis.
D) Activating Pyruvate Dehydrogenase to prevent Acetyl-CoA formation.
23. A drug specifically inhibits the transport of ADP into the mitochondrial matrix. The most likely immediate consequence would be:
A) A sustained increase in the rate of O2
B) An immediate decrease in the pH of the Intermembrane Space.
C) Stimulation of the Malate-Aspartate shuttle to compensate for energy loss.
D) Inhibition of both ATP synthesis and the ETC due to a lack of an ADP acceptor.
24. The Malate-Aspartate shuttle is the primary mechanism for transporting NADH electrons into the Mitochondria in the heart and liver. The key feature of this shuttle that makes it highly efficient is:
A) It uses Malate and Aspartate transporters, which are both uniports.
B) It converts cytosolic NADH to mitochondrial FADH2, yielding 3.5 ATP per NADH.
C) The overall transport is electrically neutral and is independent of the proton gradient
D) It converts cytosolic NADH to mitochondrial NADH, yielding 2.5 ATP per NADH.
25. Assertion (A): The hydrolysis of ATP is a highly exergonic reaction and releases a large amount of energy that powers cellular work.
Reason (R): The large negative free energy change is primarily due to the greater stability of the products ADP and Pi, which is achieved through greater resonance stabilisation and reduced electrostatic repulsion.
A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation for (A).
B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is NOT the correct explanation for (A).
C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
*****
Previous: Biophysical Chemistry Core Concepts
Next: Enzyme Kinetics and Catalysis Basics
References
- Nelson, David L. & Cox, Michael M. (2021). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, W. H. Freeman, 8th Edition
- Voet, Donald, Voet, Judith G., & Pratt, Charlotte W. (2018). Voet’s Principles of Biochemistry, Wiley, 5th Edition
- Berg, Jeremy M., Tymoczko, John L., & Stryer, Lubert (2023). Biochemistry, W. H. Freeman, 10th Edition
- Palmer, Trevor & Bonner, Philip L. (2007). Enzymes: Biochemistry, Biotechnology, Clinical Chemistry, Horwood Publishing, 2nd Edition
- Upadhyay, Avinash, Upadhyay, K., & Nath, Nirmalendu (2023). Biophysical Chemistry: Principles and Techniques, Himalaya Publishing House, 4th Edition
🔗 Explore More MCQs:

